Nucleic acid amplification assay (PCR) for the detection of Chlamydia trachomatis DNA.
This is performed as a paired test with Neisseria gonorrhoeae PCR
Diagnosis of Genital Chlamydia – Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections in the UK; it is caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.
Eye swabs can also be tested on neonates suspected of having opthalmia neonatorum.
Swabs – Endocervical /low vaginal/ rectal/ throat/urethral/ high vaginal swabs
Urine (Preferably Males only – lower sensitivity than swabs for Females)
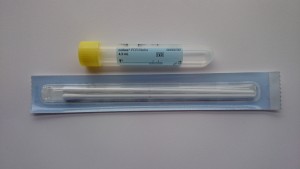
Yellow topped Chlamydia swabs (Cobas PCR)
White Top Universal Pots (20-30ml of initial stream urine)
For electronic requesting using EPIC (RDUH ONLY):
Search for: ‘Chlamydia trachomatis & Neisseria gonorrhoeae PCR‘ or test code ‘LAB1379‘
Products containing carbomer(s), including vaginal lubricants, creams and gels may interfere with the test and should not be used during or prior to collecting urogenital specimens.
The specimen collection kit consists of a paper packet containing 2 swabs and a yellow topped plastic tube containing transport media.
1. Open the plastic bag. Open the paper packet which contains two swabs. Throw away the thin ended swab – you need to use the THICKER swab ONLY.
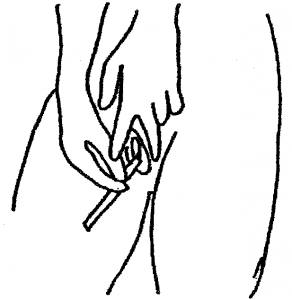
2. Stand with your feet apart and your knees bent, or sit down with your knees apart.
3. Take the thicker of the two swabs by the non-fluffy end. With your free hand hold open the skin around the vaginal opening.
4. Place the soft swab tip into the vagina approximately the length of your finger. Rotate the swab all the way around the vagina. Remove the swab and continue to hold it. Do not put it down.
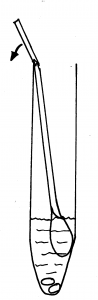
5. Holding the yellow topped tube upright, unscrew the cap and put the swab inside with the fluffy end down. There is a faintly scored ring around the white stick about 2/3 of the way up. Hold the swab stick firmly with the score mark against the top of the tube; bend it until it breaks off at the top of the tube. (There is liquid in the tube – DO NOT pour this away as it is meant to be there, without it the specimen cannot be processed.)
6. Screw the cap on firmly. Label the tube with your full name, date of birth and the date of the sample. Ensure that the tube only contains the thicker swab. The laboratory will not be able to process the sample if both swabs are in the tube.
7. You may discard the broken stick, packaging and unused swab into a household rubbish bag.
Caused by a subset of C. trachomatis (Serovars L1, L2 or L3), which can cause a more severe infection (attacking lymph nodes, causing inflammation and invasive disease.)
LGV testing is performed by the Bacteriology Reference Department, UKHSA Colindale – UKHSA – Referral form for LGV Testing
For further information on LGV – Terrence Higgins Trust – LGV
Processed locally in Microbiology at RDUH
LGV testing: Sent to Sexually Transmitted Infections Reference Laboratory (STIRL), UKHSA Colindale, London
Please allow up to 6 days for result
LGV testing: Please allow up to 7 days after sending to STIRL
Do not repeat this test within 1 month.
Routine Testing: Roche Cobas 6800
Urgent Testing: Cepheid GeneXpert
Chlamydia – Devon Sexual Health
Chlamydia – Lab Tests Online UK
Chlamydia: surveillance, data, screening and management – UKHSA
British Association for Sexual Health and HIV
National Chlamydia Screening Programme (NCSP) – UKHSA
The National Chlamydia Screening Programme offers annual (or on change of sexual partner) opportunistic screening to all sexually active men & women under 25 years.
(Sounds Like: Chlamidia)
Specimen Labelling Procedure